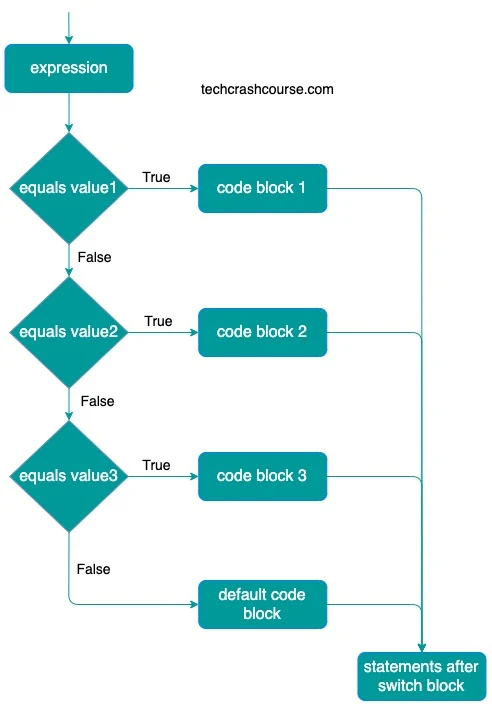
A switch statement in java allows us to selectively execute a block of statements based on the value of a variable or constant expression. In a switch case statement a variable or value of an constant expression is tested for equality against a list of possible case labels and when match is found, the block of code associated with matched case is executed.
It is similar to if..else ladder statement, but the syntax of switch statement is more readable and easy to understand. It provides a cleaner and more concise alternative to long sequences of if-else if statements, especially when dealing with scenarios where the expression can take on distinct values.
In this comprehensive tutorial, we will explore the syntax, usage, best practices, and some advanced features of the switch-case statement in Java.
Syntax of Switch Statement in Java
The basic syntax of the switch-case statement in Java is as follows:switch(expression) {
case value1 :
statements; // Code block 1
break;
case value2 :
statements; // Code block 2
break;
case value3 :
statements; // Code block 3
break;
default :
statement; // Default code block
}
- switch : The switch keyword initiates the switch-case statement.
- expression : expression is the value being tested against each case.
- case : Each case represents a possible value of the expression.
- break : The break statement is crucial to exit the switch block after executing the corresponding case. If omitted, the execution will continue to the next case.
First of all, expression is evaluated and it's value is compared with the values of each case.
- If the value of expression equals to value1, the code of case value1 will be executed.
- If the value of expression equals to value2, the code of case value2 will be executed.
- If the value of expression equals to value3, the code of case value3 will be executed.
- If the value of expression doesn't match wull any case values then the default code block will be executed.
Java Switch Case Statement Example Program
public class SwitchCaseStatement {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10, b = 5;
char operator = '*';
System.out.println("a = " + a + ", b = " + b);
switch (operator) {
case '+':
System.out.println("a+b = " + (a + b));
break;
case '-':
System.out.println("a-b = " + (a - b));
break;
case '*':
System.out.println("a*b = " + (a * b));
break;
case '/':
System.out.println("a/b = " + (a / b));
break;
default:
System.out.println("Invalid Operator");the
}
}
}
Output
a = 10, b = 5 a*b = 50
In above program, we are using switch case statement to perform arithmetic operation between variable a and b based on value of character variable operator. The value of the operator variable will be compared with each case value and the code block of the matching case will execute.
In above example, the value of operator variable is "*", which matches with the third case value and the product of a and b is printed.
Enumerations in Switch-Case
Java enums can be used effectively with switch-case statements, providing a clean and type-safe way to handle different cases. Enumerations are commonly used to represent a fixed set of constants.
public class EnumSwitchExample {
enum Day {
MONDAY, TUESDAY, WEDNESDAY, THURSDAY, FRIDAY, SATURDAY, SUNDAY
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Day today = Day.WEDNESDAY;
switch (today) {
case MONDAY, TUESDAY, WEDNESDAY, THURSDAY, FRIDAY:
System.out.println("Weekday");
break;
case SATURDAY, SUNDAY:
System.out.println("Weekend");
break;
}
}
}
In this example, the program categorizes the day into either a "Weekday" or "Weekend" based on the enumeration constant.
Important points about Switch Case Statement
- The expression in switch case must evaluates to char, byte, short, int or enum.
- You can use any number of case labels within a switch. Case labels must be unique. We cannot write two case blocks with same constants.
- Switch case performs only equality check of the value of expression/variable against the list of case values.
- The default code block gets executed when none of the case matches with expression. default case is optional and doesn't require a break statement.
- The break statement is optional.The break statement at the end of each case cause switch statement to exit. If break statement is not used, all statements below that case statement are also executed until it found a break statement.
- One switch statement can have maximum of one default label. Default block can be placed anywhere in switch statement.
Best Practices of Using Switch-Case Statements
- Use switch for Multiple Conditions : If you have multiple conditions based on the value of a single variable, prefer using a switch-case statement for better readability and maintainability.
- Use Enums for Constants : If your cases involve a fixed set of constants, consider using enums. This ensures type safety and makes your code more readable.
- Keep Each Case Simple : Each case block should contain a simple set of instructions. Avoid complex logic within a case block for better maintainability.
- Provide a Default Case : Always include a default case to handle unexpected values. This helps in debugging and prevents silent failures.
- Avoid Fall-Through Unless Intentional : Generally, use break to terminate each case block. Avoid fall-through unless it is intentional and well-documented.
- Test Your Switch Statements : As with any code, thoroughly test your switch-case statements to ensure they behave as expected under various conditions.
Switch statements can only be used to perform equality comparison, we cannot perform conditional checks using relational or logical operators like <, >, <=, &&, || etc.
Conclusion
The switch-case statement in Java is a valuable tool for handling multiple conditions based on the value of an expression. Whether dealing with numeric values, enums, or strings, the switch-case statement provides a clean and efficient way to structure your code. By adhering to best practices, such as using enums for constants, keeping each case simple, and providing a default case, you can create readable and maintainable code. Understanding the nuances of fall-through, testing your switch statements thoroughly, and choosing when to use switch versus if-else if are essential skills for any Java developer.
