The for loop in C++ is used to execute execute some statements repetitively until the given condition is true. The for loop is mainly used to perform repetitive tasks.
Syntax of for Loopfor(initialization; condition; update) {
/* code to be executed */
}
For Example:
for(i = 1; i <= 10; i++){
cout << i;
}
Above for loop prints integers from 1 to 10;
For Loop Syntax Description
- Initialization : The Initialization statement allows us to declare and initialize any loop variables. It is executed only once at the beginning of the for loop.
- Condition : After initialization, condition expression is evaluated. It is a boolean expression which decides whether to execute loop's body or terminate for loop. if condition expression evaluates to true, the for loop code block gets executed otherwise it will terminate for loop and control goes to the next statement after the for loop.
- Update : After code block of for loop gets executed, control comes back to update statements. It allow us to modify any loop variable for next iteration of loop. This step is mainly used for updating loop control variable.
- All three fields of a for loop are optional. They can be left empty, but in all cases the semicolon signs between them are required.
Control Flow Diagram of for loop
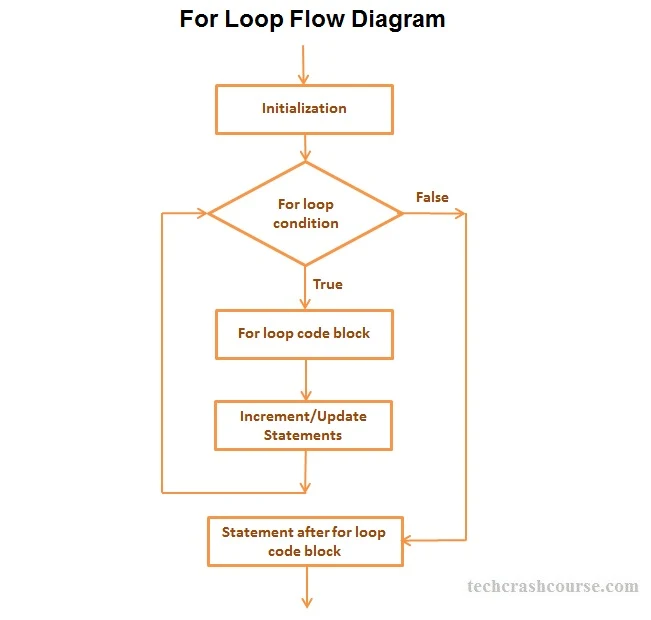
- The Initialization statement will be executed first. We can declare and initialize any number of loop control variables here.
- After the Initialization statement the condition expression is evaluated. If the value of condition expression is true then code block of for loop will be executed otherwise the loop will be terminated.
- After execution of the code block of for loop control goes to update statements of the loop statement which modifies the loop control variables.
- After modifying control variables in update statements, control again goes to condition expression.
- For loop iteration continues unless condition expression becomes false or for loop gets terminated using break statement.
Advantages of the For Loop in C++
- Initialization Within the Loop : The for loop allows the declaration and initialization of the loop control variable within the loop statement itself. This feature limits the scope of the loop control variable to the loop block, minimizing its visibility outside the loop. It aligns with the best practice of keeping variables as localized as possible. This encapsulation helps avoid unintended side effects and potential naming conflicts.
- Efficient Iteration with Indexing : For loops are particularly well-suited for iterating over arrays or other sequences where index-based access is required. The loop control variable acts as the index, providing a natural and efficient means of traversing elements. The direct correlation between the loop control variable and array indices simplifies code for tasks like accessing array elements, making it more intuitive and efficient.
- Ease of Modification : The for loop's distinct sections make it easy to modify the initialization, condition, or update expressions without affecting the loop's overall structure. This flexibility allows developers to adapt the loop to changing requirements or fine-tune its behavior without extensive modifications.
- Ideal for Count-Controlled Loops : For loops excel in count-controlled scenarios where the number of iterations is known in advance. The loop's initialization, condition, and update expressions align naturally with the concept of counting iterations. This makes for loops an ideal choice for tasks where a specific count or range determines the iteration flow.
- Smooth Integration with Algorithms : The for loop seamlessly integrates with various algorithms and operations. Whether applying a transformation to each element in an array or performing a specific action for a set number of iterations, the for loop's versatility shines when combined with standard algorithms or custom logic.
C++ for Loop Example Program
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int N, i, sum=0;
cout << "Enter a positive number\n";
cin >> N;
// Using for loop to find the sum
// of all integers from 1 to N
for(i=1; i <= N; i++){
sum+= i;
}
printf("Sum of all numbers from 1 to %d = %d", N, sum);
return 0;
}
Output
Enter a positive number 6 Sum of all numbers from 1 to 6 = 21In above program, we first take a number N as input from user. Now, we have to find sum of all numbers from 1 to N. We are using a for loop to iterate from 1 to N and add each number to variable sum.
- The condition_expression in for loop is a boolean expression. It must evaluate to true or false value(In C++, all non-zero values are considered as true and zero is considered as false).
- Initialization statement, Condition expression and Update statement are all optional in for loop.
- You can use multiple initialization statements and update statements inside for loop.
For Example:
for(i=0, j=50; i < 100; i++, j--) - Opening and Closing braces are not required for single statement inside for loop code block.
For Example:
for(i = 0; i < 100; i++)
sum+= i; - We can also use infinite for loops like for(;;), which will never terminate. You should add terminating condition using break statement in order to terminate infinite for loop.
For Example:
for(;;){
if(.....){
break;
}
}
Best Practices for Using For Loops
- Use Meaningful Variable Names : Choose variable names that convey the purpose of the loop control variable. This enhances code readability.
for (int day = 1; day <= 7; ++day) { // Code for each day of the week } - Limit the Scope of the Loop Control Variable : Declare the loop control variable within the for loop if it's only needed within that scope. This minimizes its visibility and reduces the chance of unintended side effects.
- Use Pre-Increment/Decrement for Efficiency : Pre-increment (++i) and pre-decrement (--i) are generally more efficient than their post counterparts. While modern compilers can often optimize, using pre-increment is a good habit.
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) { // Code within the loop } - Avoid Changing the Loop Control Variable Inside the Loop : Modifying the loop control variable within the loop can lead to confusion and unexpected behavior. Stick to updating it in the update expression.
- Consider Range-Based For Loop for Containers : When iterating over the elements of a container, especially in C++11 onward, consider using the range-based for loop for a more concise syntax.
- Be Mindful of Infinite Loops : Ensure that the condition in the for loop eventually becomes false to prevent unintentional infinite loops.
for (int i = 0; i < 5; --i) { // This will result in an infinite loop }
Conclusion
You've successfully navigated the seas of for loops in C++. You now possess the skills to traverse arrays, handle matrices, and dance through the elements of containers with grace and precision.
As you continue your coding expedition, remember that the for loop is not just a tool; it's a versatile instrument in your arsenal. Use it wisely, and it will guide your code through the rhythm of repetition with elegance.
