Do..While loop in java is similar to while loop except do-while loop evaluates its condition expression after the execution of loop code block. Do..While loop in java is used to execute a block of code multiple times.
Do while loop ensures that that code block inside do-while body will execute atleast once. As the condition expression check is after do-while loop code block, it first execute it's code block and then decide whether to iterate again or not.
By the end of this tutorial, you'll have a solid understanding of how to effectively leverage the do-while loop in your Java programs.
Understanding the Basic Syntax of do-while Loop
do {
// do while loop code block
statement(s);
} while(condition);
- statement(s); : This block of code is executed at least once.
- condition : The loop continues to execute as long as this boolean expression evaluates to true. If the condition becomes false, the loop terminates.
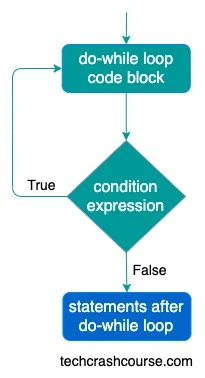
Control flow of do-while loop
condition expression is a boolean expression which gets evaluated every time after loop code block. Here is the description of do..while loop control flow.
- First of all, do-while loop code block gets executed.
- do-while loop evaluates condition expression inside the parenthesis.
- If condition expression evaluates to true, then do-while loop code block gets executed.
- condition expression is evaluated again.
- This execution process continues until the condition expression evaluates false.
- Whenever condition expression evaluates to false, do-while loop terminates and control goes to the next statement after the do-while loop.
Here is the flowchart of do-while loop execution
Java Do-While Loop Example Program
public class DoWhileLoop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = 0;
do {
System.out.println(count);
count++;
} while(count < 5);
}
}
Output
0 1 2 3 4
In above program, do-while loop executes code block 5 times, till the time the value of count variable is less than 5. With each iteration the value of count variable is incremented. As soon as value of count becomes 5 do-while loop terminates.
Here are the execution steps for each iteration of do-while loop in above program.
| Iteration Count | Variable | Do-While Code Block | Condition(count < 5) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | count = 0 | Print count(0). count is incremented to 1 |
true |
| 2 | count = 1 | Print count(1). count is incremented to 2 |
true |
| 3 | count = 2 | Print count(2). count is incremented to 3 |
true |
| 4 | count = 3 | Print count(3). count is incremented to 4 |
true |
| 5 | count = 4 | Print count(4). count is incremented to 5 |
false |
Best Practices of Using Array Data Structures
- Ensure an Exit Condition : Always ensure that there's a clear exit condition to prevent infinite loops. A do-while loop guarantees at least one execution, but it can still become infinite if the exit condition is never met.
- Initialize Variables Outside the Loop : Initialize loop control variables outside the do-while loop to avoid unintentional reinitialization inside the loop.
- Increment or Decrement Inside the Loop : Increment or decrement loop control variables inside the loop to avoid unintentional infinite loops or skipped iterations.
- Use break Sparingly : While the break statement can be useful for exiting a loop prematurely, excessive use can make the code harder to understand. Consider refactoring the loop or using additional conditional statements to improve clarity.
- Be Mindful of Initialization : Ensure that any variables used in the loop condition are properly initialized before the loop. Failure to initialize variables may result in compilation errors.
- Keep Loop Body Simple : Keep the body of the do-while loop simple and avoid complex logic. If the loop body becomes too complex, consider refactoring the code into separate methods.
Advanced Do-While Loop Techniques
- Nested Do-While Loops : Just like while loops, do-while loops can also be nested to handle more complex scenarios.
public class NestedDoWhileLoopExample { public static void main(String[] args) { int outer = 1; do { int inner = 1; do { System.out.println("Outer: " + outer + ", Inner: " + inner); inner++; } while (inner <= 3); outer++; } while (outer <= 3); } }In this example, the outer do-while loop executes three times, and for each iteration of the outer loop, the inner do-while loop executes three times, producing a total of nine output lines. - Do-While Loop for String Manipulation : do-while loops can be employed for string manipulation tasks, such as reversing a string.
public class ReverseStringDoWhileExample { public static void main(String[] args) { String original = "Hello, World!"; String reversed = ""; int index = original.length() - 1; do { reversed += original.charAt(index); index--; } while (index >= 0); System.out.println("Original: " + original); System.out.println("Reversed: " + reversed); } }In this example, the do-while loop iterates through the characters of the original string in reverse order, creating a reversed string. - Infinite Do-While Loop with a Break : You can create an infinite do-while loop and use a break statement to exit the loop based on a certain condition.
public class InfiniteDoWhileLoopExample { public static void main(String[] args) { int count = 1; do { // Code count++; if (count > 5) { break; } } while (true); } }In this example, the do-while loop is intentionally infinite, and the break statement is used to exit the loop when the count exceeds 5.
Conclusion
The do-while loop in Java is a valuable tool for scenarios where you want to guarantee the execution of a block of code at least once. By mastering the basic syntax, understanding use cases, adopting best practices, and exploring advanced techniques, you can use the do-while loop effectively in your Java programs.
As you continue to develop your Java programming skills, practice using do-while loops in various scenarios. Whether you're building interactive menu-driven programs, validating user input, or processing collections, the do-while loop provides a robust and flexible solution. Consistent practice and adherence to best practices will enhance your ability to write clean, efficient, and maintainable code using do-while loops in Java.
